Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
Identify, locate, and describe the origin, insertion and function of the muscles of the thorax.
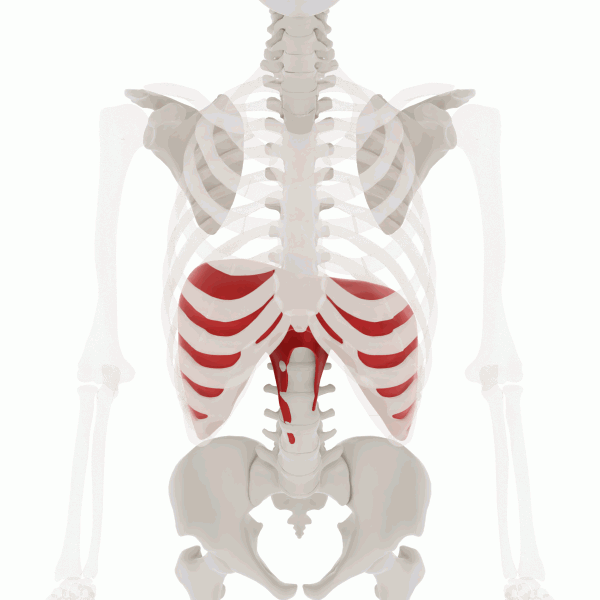
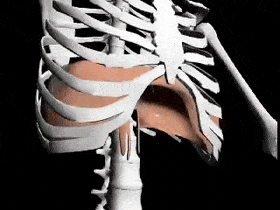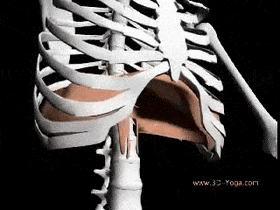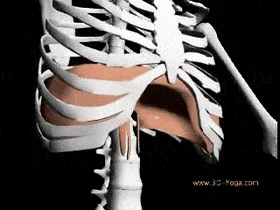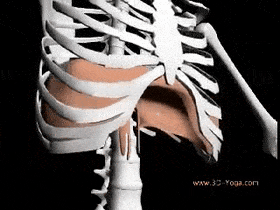
The muscles of the chest serve to facilitate breathing by changing the size of the thoracic cavity. When you inhale, your chest rises because the cavity expands. Alternately, when you exhale, your chest falls because the thoracic cavity decreases in size.
Breathing involves two events: inspiration (inhalation), when the air moves into the lungs and expiration (exhalation), when the air leaves the lungs.
We will consider the following three muscles of the thorax:
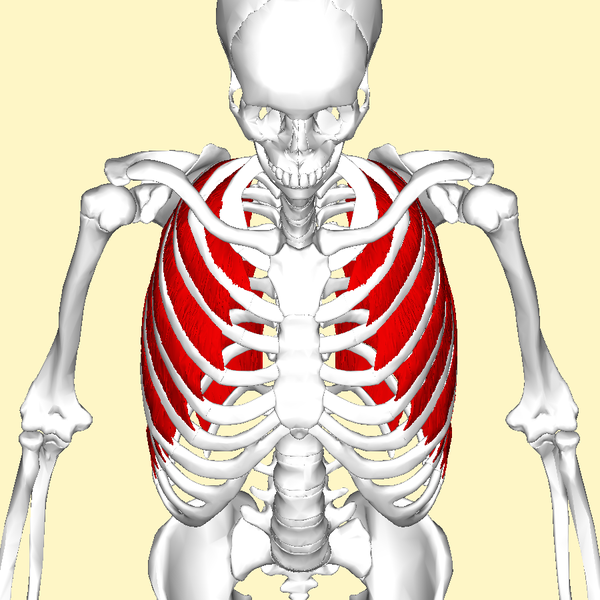
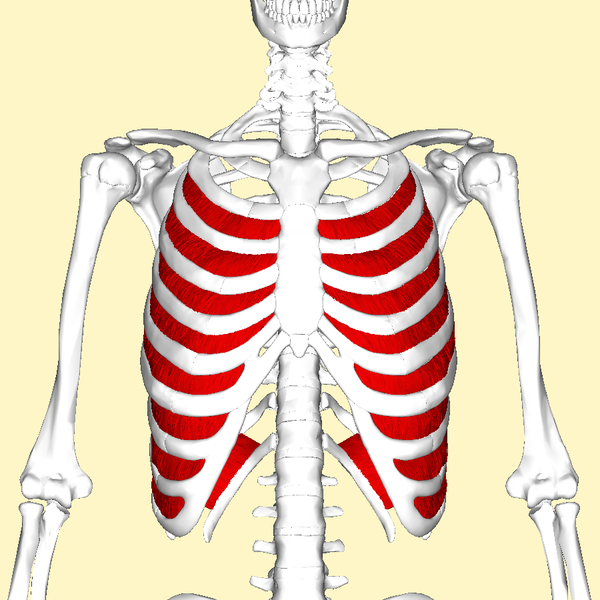
- External intercostals
- Internal intercostals
- Diaphragm
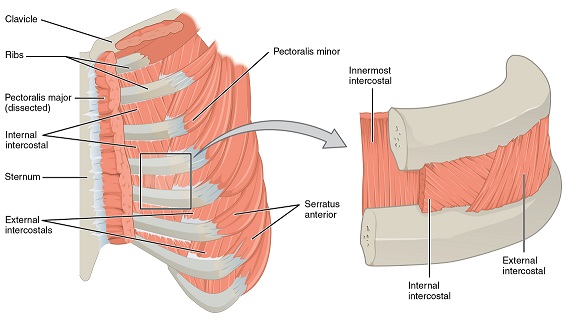
The relative positions and arrangement of the internal and external intercostal muscles can be seen in the figure below. The external intercostals are located laterally on the sides of the body. The internal intercostals are located medially near the sternum.
Watch the video below on the muscles of the thoracic wall (12:33 min).
Test Your Knowledge
Now it’s your turn! Use the interactive activities below to test your knowledge of muscles of the thorax (and shoulder).